Navigating 2025’s Economic Challenges: Essential Insights for U.S. Credit Union Executives to Boost Growth and Success
Understanding the 2025 Global Economic Outlook: Key Considerations for U.S. Credit Union Executives
As 2025 unfolds, U.S. credit union executives must navigate a rapidly shifting global economic landscape. The interplay between economic growth, persistent inflation, labor market shifts, and evolving regulatory requirements is shaping an operating environment marked by both opportunity and heightened risk. Decision-makers need timely insights to align strategies with emerging trends and ensure the long-term success of their institutions.
The Global Economic Backdrop: Moderate Growth Amid Headwinds
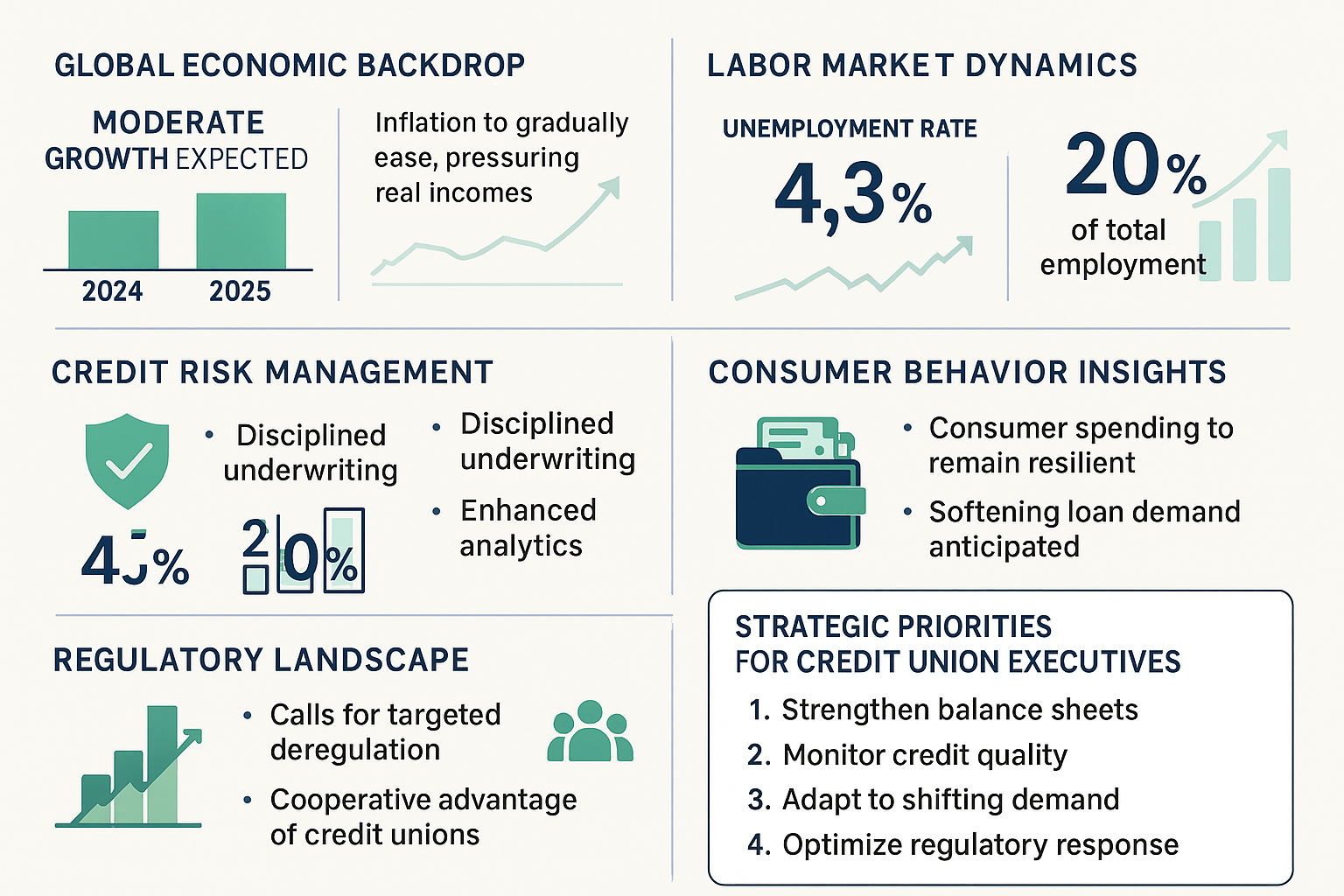
After a resilient performance in 2024, the global economy is showing signs of moderation. U.S. GDP growth, projected to settle around 2% in 2025—slightly below the previous year’s 2.4%—reflects the ongoing impact of tighter monetary policy and lingering uncertainty across major economies. According to analyses from AP News and global financial reporting from the Wall Street Journal, these themes echo across regions, with advanced and developing economies both confronting inflationary pressures and cautious investment climates.
The International Monetary Fund and leading financial institutions have highlighted that higher interest rates and persistent inflation are dampening credit expansion and slowing consumer spending worldwide. In the U.S., consumer demand remains relatively robust, buoyed by improving real wages and healthy debt-to-income ratios. However, as the GoWest Association notes, this resilience comes against the backdrop of elevated living costs and tight labor markets, both of which pose structural challenges for U.S. consumers and financial service providers.
Inflation, Interest Rates, and Their Impact on Credit Unions
Inflation remains a top concern for policymakers and credit union executives alike. Despite signs of slowing price increases, expectations remain high amid volatile energy markets and shifting supply chains. The Federal Reserve’s cautious approach has resulted in fewer and slower interest rate cuts than previously anticipated, maintaining pressure on borrowing costs across the spectrum.
For credit unions, persistently high rates present a double-edged sword. While they can bolster net interest margins, they also raise the cost of funds for members, potentially impacting loan demand and the affordability of credit products. The CNBC World Economy desk reports that ongoing inflation will continue to influence consumer sentiment, with many households delaying discretionary purchases and seeking out more favorable loan terms—trends that credit unions must monitor closely to adjust their lending strategies and risk management frameworks.
Labor Market Dynamics: Opportunities and Risks
The U.S. labor market remains historically tight, but cracks are starting to appear. Unemployment has ticked up to 4.1%, with full-time job growth flattening and part-time employment on the rise. This shift places new financial strains on many households, as reported by sources tracking the broader economy. For credit unions, the evolving job market brings both risks and opportunities: on one hand, a flexible workforce supports economic participation; on the other, stagnant wages and the growth in part-time work can exacerbate member vulnerability and increase credit risk.
Credit unions are uniquely positioned to offer member-focused solutions—such as income smoothing loans and flexible payment plans—that address these new realities. However, proactive monitoring of local employment trends and close engagement with at-risk members will be essential to sustaining portfolio quality and supporting community stability.
Credit Risk Management in a Slower Growth Environment
With GDP growth slowing to a consensus range between 1.0% and 2.0%, credit risk management rises to the top of the agenda for credit union leaders. A recent analysis by Plante Moran highlights that credit quality is expected to “return to normal,” with modest increases in delinquencies and net charge-offs compared to historically low levels seen in preceding years.
Particular attention must be paid to certain loan segments experiencing heightened stress. Commercial real estate portfolios—especially office properties—continue to face elevated vacancies and downward pressure on valuations, while agricultural loans face headwinds due to lower commodity prices and rising input costs. In commercial and industrial lending, risk is elevated in niches like retail (including motor vehicle dealers and electronics), transportation, healthcare, and waste management services.
For credit unions, timely identification of emerging risks and disciplined underwriting are crucial. Enhanced analytics, stress-testing, and diversified portfolios can help mitigate losses and provide the agility needed to respond to changing economic conditions.
Consumer Behavior: Spending Patterns and Loan Demand
Despite economic headwinds, consumer spending remains a cornerstone of the U.S. economy. Healthier balance sheets and rising real incomes are expected to keep loan growth on track, with forecasts suggesting total loan growth could reach 6% in 2025. As highlighted by the CreditUnions.com 2025 outlook, consumer confidence is likely to stay positive, provided inflation is kept in check and labor market conditions do not deteriorate further.
However, rising treasury yields and higher borrowing costs could moderate demand for mortgages, auto loans, and other big-ticket items. Credit unions may also see shifts in deposit mix as members seek higher yields, favoring term certificates or money market accounts over traditional savings.
Regulatory Developments and the Cooperative Advantage
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with calls for targeted deregulation aimed at reducing compliance burdens for small businesses and financial cooperatives. As noted in the 2025 Global Regulatory Update from the World Council of Credit Unions, appropriate regulation is essential not only for financial stability but also for promoting access to credit and fostering economic growth. Industry experts suggest that a balanced approach—enabling innovation while protecting consumers—will be central to the continued relevance of credit unions in a competitive marketplace.
Credit union leaders have an opportunity to leverage their unique cooperative structure to advocate for sensible regulation and to differentiate themselves on the basis of member service, transparency, and community engagement.
Strategic Priorities for Credit Union Executives in 2025
To thrive in the complex global economic landscape of 2025, credit union executives should focus on several strategic priorities:
– Strengthen risk management frameworks by integrating real-time data and stress-testing capabilities.
– Deepen member relationships through targeted financial wellness programs and personalized service.
– Embrace digital transformation to enhance efficiency, accessibility, and resilience.
– Invest in staff training to adapt to regulatory changes and emerging member needs.
– Advocate for regulatory environments that support innovation while safeguarding systemic stability.
By staying agile, U.S.-based credit unions can not only navigate the ongoing economic uncertainties but also emerge as trusted community anchors, driving financial inclusion and sustainable growth in the years ahead.